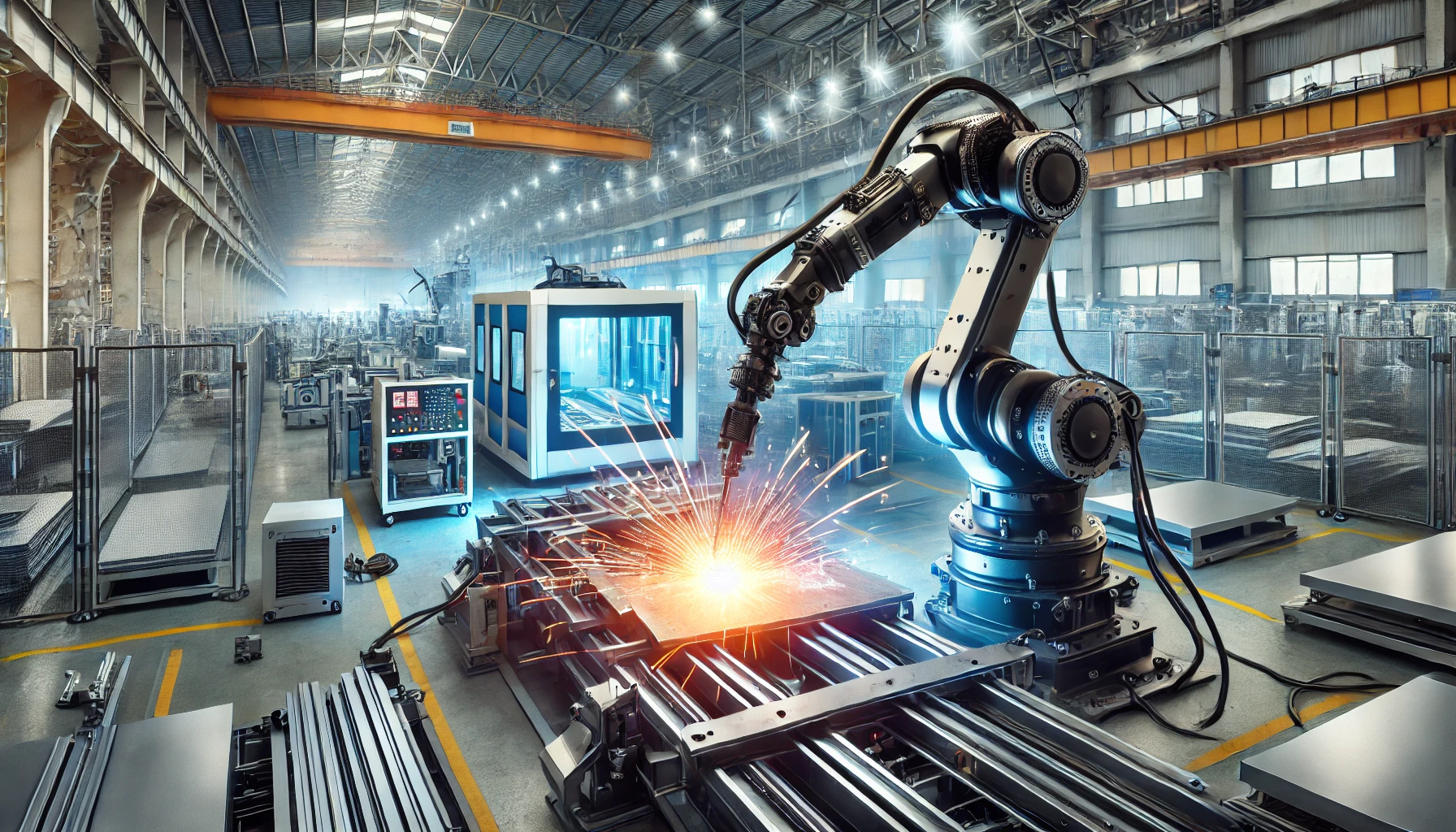
Welding is a common technique used in the manufacturing industry to create structures, products, and components.
Welding is a process of joining two or more pieces of metal or thermoplastics together by heating the surfaces to their melting points, causing them to fuse and form a strong bond. The process of welding can be achieved through various methods, including gas welding, laser welding, arc welding, and resistance welding.
There are several different types of welding techniques that can be used in manufacturing, including:
- Arc welding – this technique involves using an electric arc to create heat and melt the metal, which is then fused together as it cools.
- Gas welding – this method uses a flame generated by burning a fuel gas, such as acetylene, to melt and join the metal.
- Resistance welding – this technique uses electrical resistance to heat and melt the metal, which is then joined together under pressure.
- Laser welding – this process uses a high-powered laser beam to melt and join the metal together.
Each welding technique has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique will depend on the specific needs of the manufacturing process. Some factors to consider when choosing a welding technique include the type of materials being joined, the size and shape of the components, and the production requirements.
Gas welding involves heating the metal to be welded with a flame and then adding a filler material to create a strong bond. Arc welding uses an electric arc to heat the metal and melt the filler material, creating a strong bond. Resistance welding involves using an electrical current to heat the metal, causing it to melt and fuse together.
Welding is commonly used in manufacturing, construction, and repair work to create and repair metal structures, pipes, and machinery. Proper safety measures must be taken when welding, including wearing protective clothing and using appropriate ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
Here are some common do’s and don’ts of welding:
DO:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as a welding helmet, gloves, and long-sleeved clothing to protect yourself from sparks, ultraviolet radiation, and other hazards.
- Ensure that your work area is well-ventilated and free of any flammable materials that could catch fire during welding.
- Keep your welding equipment and tools clean and well-maintained to ensure safe and effective operation.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using welding equipment, and ensure that you have received proper training and certification before attempting to weld.
- Check the ground connection and electrode holder for proper connections and clean them regularly to ensure a good electrical contact.
- Inspect the materials you will be welding for any defects or cracks that could cause a weakened joint or failure.
DON’T:
- Do not weld in areas with inadequate ventilation, or where there are flammable materials nearby.
- Do not attempt to weld materials that are incompatible, such as welding stainless steel to carbon steel without proper preparation and technique.
- Do not overlook the importance of PPE, as it can protect you from serious burns, eye injuries, and other hazards associated with welding.
- Do not leave your welding equipment unattended, and ensure that it is turned off and properly stored when not in use.
- Do not weld on materials that are painted, coated, or contain other contaminants without first removing them, as these can produce toxic fumes and weaken the weld joint.
- Do not weld on materials that have not been properly cleaned or prepared, as this can result in weak and unreliable welds.
For help on welding aluminum, contact us, and we will be willing to help. Read our blog for more tips like these.