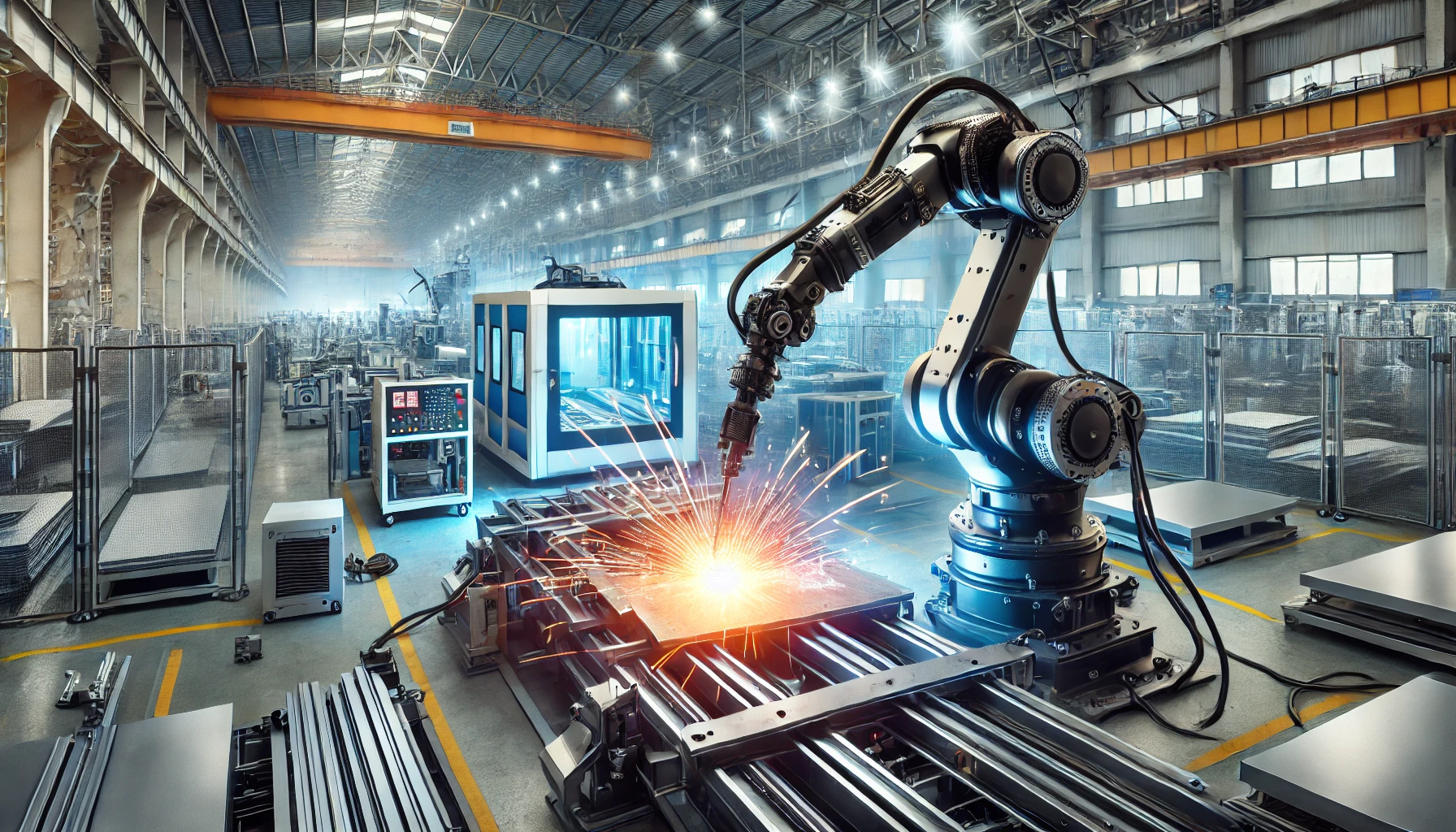
Welding has been an essential manufacturing process for centuries, used in everything from automotive production to infrastructure development. However, as industries demand higher precision, efficiency, and safety, the welding process has evolved with technological advancements. One of the most transformative innovations in recent years is the use of robotics in welding. This fusion of automation and welding has not only streamlined production but also opened the doors for entirely new possibilities in various industries.
The Role of Robotics in Welding
At its core, robotic welding involves the use of robotic arms equipped with welding equipment to perform tasks traditionally done by human welders. These robots can be programmed to execute a wide range of welding processes, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and spot welding. By integrating sensors, vision systems, and advanced software, robots can perform tasks with unparalleled precision, consistency, and speed.
Key Advantages of Robotic Welding
1. Increased Productivity
Robots can work around the clock without needing breaks or rest periods, dramatically increasing production rates. In addition, they can maintain high levels of consistency and speed, which reduces cycle time per product. This increased efficiency translates into higher output with fewer human resources, which is particularly valuable in industries like automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and heavy machinery production.
2. Improved Quality and Precision
Robotic welders are not subject to human fatigue, allowing them to maintain a consistent level of quality throughout the entire production process. The precision of robotic welding is also significantly higher than that of human welders, ensuring stronger and more uniform welds. This precision is crucial, particularly in high-stakes industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where a single flaw can have catastrophic consequences.
3. Enhanced Safety
Welding can be hazardous, with workers exposed to high heat, toxic fumes, and dangerous equipment. Robots can handle these dangerous tasks, protecting human workers from these risks. With welding robots taking over the most hazardous parts of the job, workers can focus on supervising the process or handling more complex tasks, improving overall workplace safety.
4. Cost Efficiency
While the upfront cost of implementing robotic systems can be significant, the long-term savings are substantial. Robots can lower labor costs, reduce material waste, and minimize defects, all of which contribute to a more cost-efficient production process. Additionally, robotic welding systems require less maintenance compared to manual welding, further reducing operational expenses.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability
Modern robotic welding systems are incredibly versatile. They can be easily reprogrammed to handle different types of welding tasks, making them suitable for a variety of production lines. Whether it’s welding small, intricate parts or large, complex assemblies, robots can be quickly adapted to meet the needs of different projects without requiring a complete overhaul of the system.
Applications of Robotics in Welding
Automotive Industry
One of the earliest and most prominent adopters of robotic welding was the automotive industry. Robotic arms have become an integral part of car assembly lines, where they perform tasks such as spot welding, seam welding, and MIG welding. By using robots for these processes, automakers can achieve consistent welds, reduce the weight of the vehicle by using thinner materials, and speed up production cycles—all critical factors in today’s competitive automotive market.
Aerospace
In aerospace manufacturing, precision is paramount, and even the slightest flaw in a weld can result in catastrophic failure. Robotic welders in the aerospace industry are tasked with creating strong, high-precision welds in critical components such as aircraft frames and turbine engines. These robots help meet the stringent quality standards required for aerospace applications while improving production speed.
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is another industry that benefits from robotic welding. The scale and complexity of the structures involved require highly skilled welding processes. Robotic systems can handle the repetitive and strenuous welding tasks required for ship construction, improving speed, safety, and quality in a challenging environment.
Heavy Equipment and Manufacturing
Robots are also making waves in the heavy equipment sector, where large, durable parts are welded together. Robotic welding systems can efficiently handle large-scale assemblies, creating strong and reliable welds that meet the rigorous standards of industries such as construction, mining, and energy.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of robotic welding are clear, there are also some challenges associated with its implementation. Initial investment costs for purchasing robotic systems can be high, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses. Additionally, integrating robotic systems into existing production lines may require significant adjustments, including reprogramming and updating equipment.
Moreover, while robots can handle many aspects of welding, human expertise is still needed to program, monitor, and maintain these systems. The balance between automation and human oversight remains a key consideration for companies looking to adopt robotic welding.
The Future of Robotics in Welding
The future of robotic welding looks bright, with continued advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor technology. As robots become smarter, they will be able to make real-time adjustments based on factors like material variation and environmental changes. This will further enhance the capabilities of robotic welding systems, making them even more efficient and adaptable.
Additionally, collaborative robots (cobots) are becoming more prevalent in welding applications. These robots are designed to work alongside human operators, allowing for greater flexibility and collaboration between man and machine.
Conclusion
The integration of robotics into welding is revolutionizing the way industries approach manufacturing. With the promise of increased productivity, improved quality, better safety, and reduced costs, robotic welding systems are becoming indispensable tools in many industries. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect robotic welders to become even more precise, flexible, and accessible, unlocking new possibilities and opportunities in the world of manufacturing. The future of welding is undoubtedly robotic, and it’s clear that this innovation is here to stay.
At Blackstone, use our expertise and capabilities for safe and secure welding. Get in touch with us today, and we’ll solve your problems.